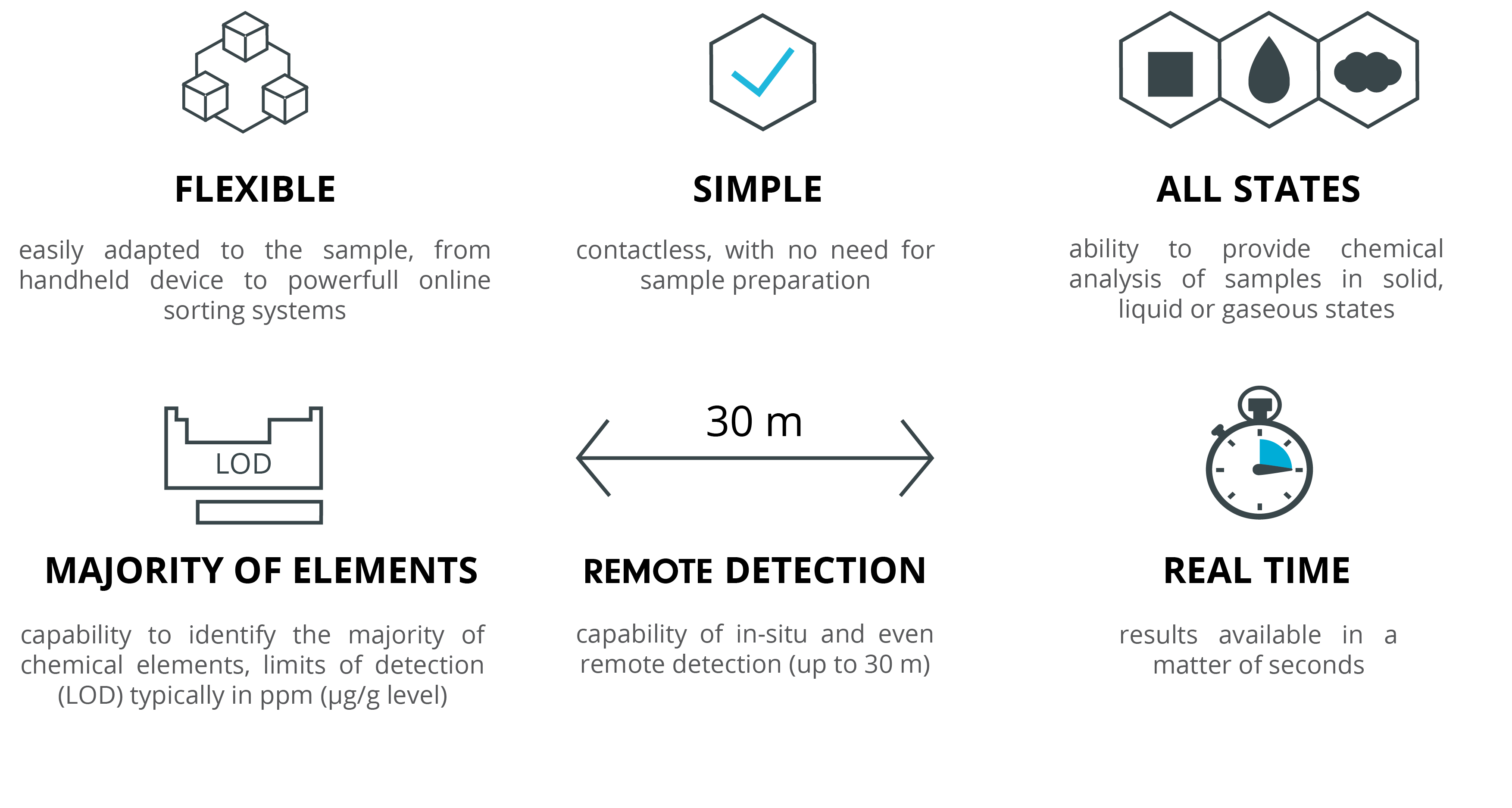
LIBS – Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
is a modern analytical technique which utilizes a laser pulse to fast determine the elemental composition of a sample. It is an effective combination of the laser ablation and the atomic emission spectroscopy.
How LIBS works?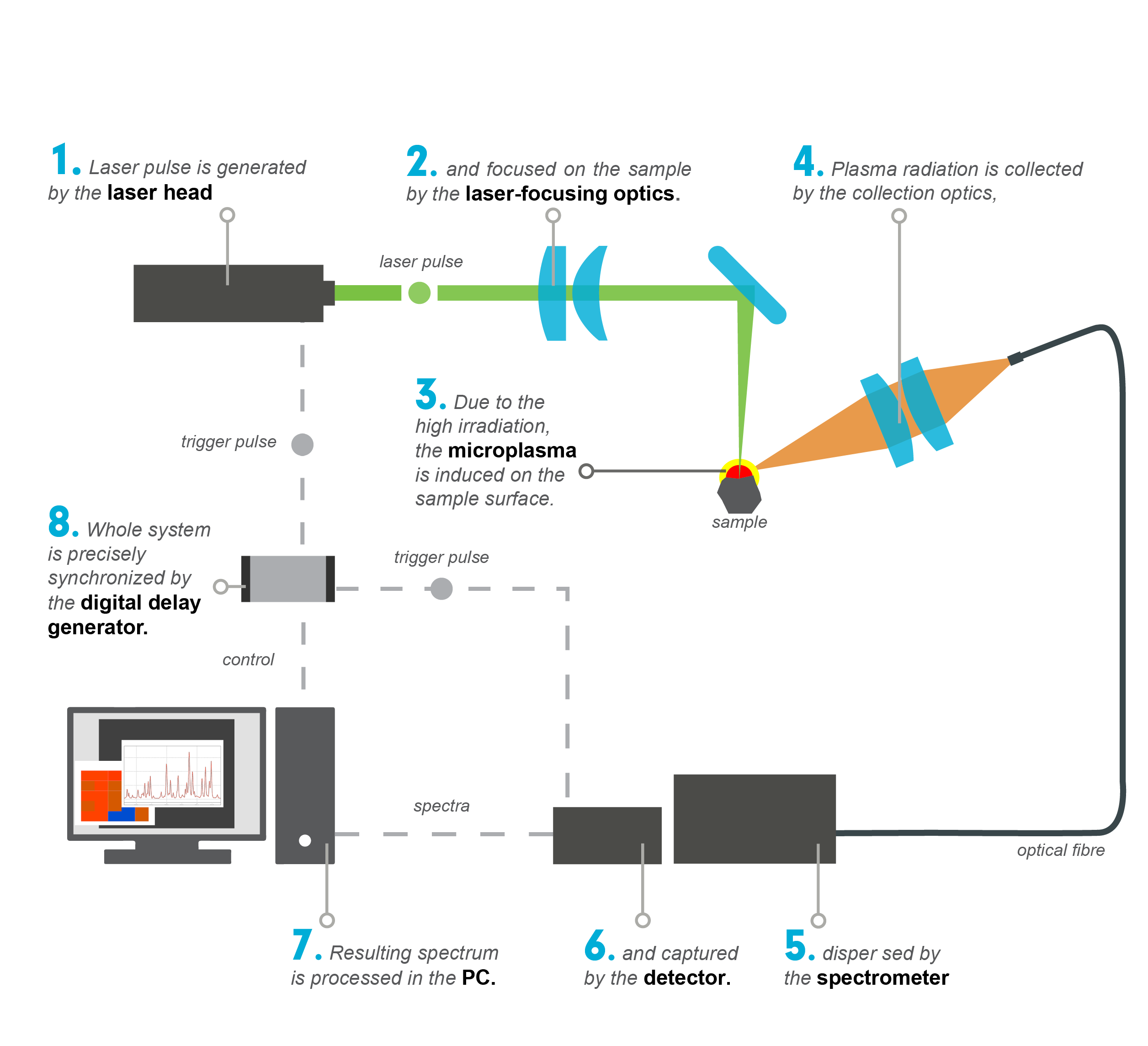
Applications
Implementation of machine learning algorithms: application of artificial neural networks (including deep learning) to meet the requirements of high nonlinearity in both quantitative and qualitative LIBS analysis;
Foundry and metallurgy: detection of C, S, P in steel; fast on-line quality control
Mining and extraterrestrial research: rock identification, quantification of trace elements
Clinical research: mapping of heavy metals’ distribution in soft and hard tissues, elemental mapping of bone scaffolds
Toxicology: influence of nanoparticles contamination on the growth of plants and small organisms - zebra fish embryos
Automotive: characterization of thin surfaces; depth profiling - selective detection of elements in material layers
Agriculture and environmental diagnostics: detection of fertilizers and toxicity contamination
Archeology, forensics (e.g. braking track detection), civil engineering (chlorine degradation of structures), etc.